Stem Cells: A Regenerative Revolution
Stem Cells: A Regenerative Revolution
In medical science, few discoveries have sparked as much excitement and promise as the discovery of stem cells. These remarkable cells possess the unique ability to develop into different types of cells in the body, holding the potential to regenerate damaged tissues, treat diseases, and fight inflammation, all while doing it from our own, unique DNA blueprint.
We are witnesses to a revolution in healthcare as we know it, and this is part of the Regenerative Medicine universe that brings us closer and closer to our younger selves. Bye, bye zombi cells!
What Are Stem Cells?
At their core, stem cells are undifferentiated cells with the remarkable ability to transform into specialized cell types with specific functions. They are the building blocks of our bodies, essential for growth, repair, and regeneration. Stem cells can be found in various tissues throughout the body, including embryonic tissue, umbilical cord blood, bone marrow, and even in some adult tissues.
Types of Stem Cells:
There are various types of stem cell biologics that we can receive in different treatments
1- Platelet Rich Plasma, or PRP, usually used for joint pain and tendonitis, thinning hair, sexual function and face cosmetology.
- Embryonic Stem Cells (ESCs):** These are derived from embryos and have the capacity to develop into any cell type in the body. They hold immense potential for regenerative medicine but are ethically controversial due to their origin.
3. Adult Stem Cells:** Also known as somatic or tissue-specific stem cells, these are found in specific tissues throughout the body and can generate cell types native to the tissue in which they reside. While not as versatile as ESCs, they still play a crucial role in tissue maintenance and repair.
4. Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs):** These are adult cells that have been reprogrammed to exhibit pluripotency, similar to embryonic stem cells. iPSCs offer the versatility of ESCs without the ethical concerns, making them a valuable tool for research and potential therapies.
Applications of Stem Cells: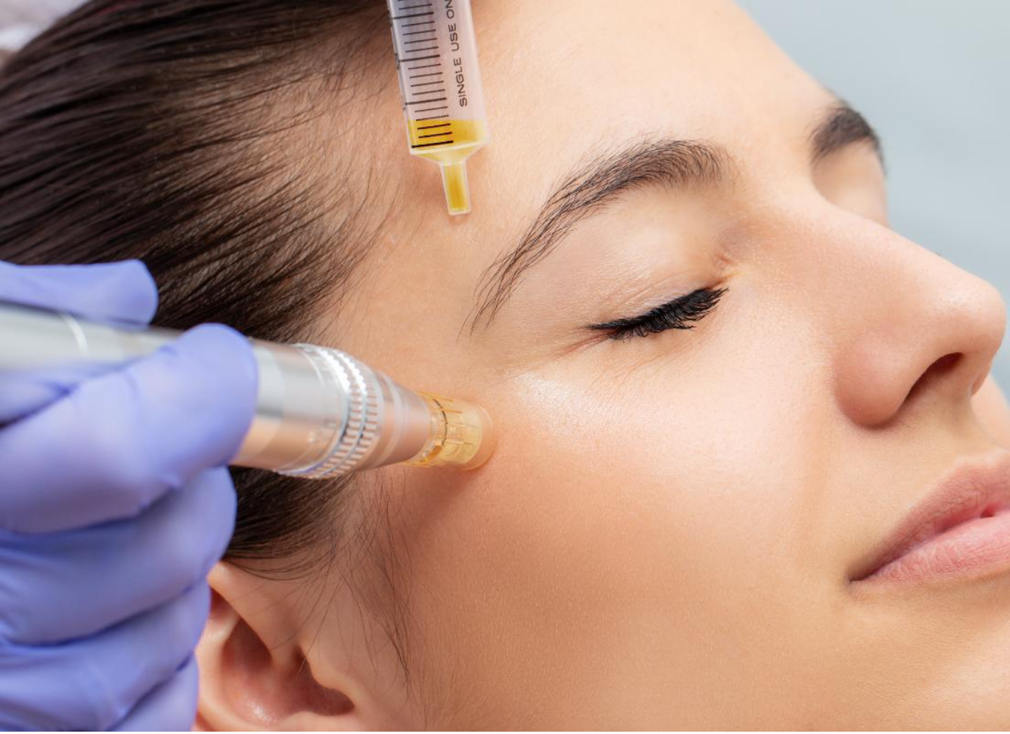
1. Regenerative Medicine: Stem cells hold the potential to regenerate damaged tissues and organs, offering hope for patients with conditions ranging from spinal cord injuries to heart disease. Researchers are exploring stem cell therapies for tissue repair and replacement, including bone, cartilage, nerve, and muscle regeneration.
2. Disease Modeling and Drug Testing: Stem cells can be used to model diseases in the laboratory, providing insights into disease mechanisms and enabling the development of more effective treatments. They also serve as a valuable tool for drug testing, allowing researchers to screen potential therapeutics in a controlled environment.
3. **Cell-Based Therapies: Stem cell-based therapies have shown promise in treating a variety of conditions, including leukemia, lymphoma, and certain genetic disorders. For example, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation has become a standard treatment for certain blood cancers and disorders.
Challenges and Considerations:
While the potential of stem cells is vast, their application is not without challenges and ethical considerations. One of the primary challenges is ensuring the safety and efficacy of stem cell therapies, as well as addressing the risk of tumor formation associated with some types of stem cells.
Ethical concerns also surround the use of embryonic stem cells, as their derivation involves the destruction of human embryos. However, advances in technology, such as the development of iPSCs, offer alternatives that mitigate these ethical concerns. At this point, exosomes seem to be the best delivery system, since they carry extremely low trace of the donor´s DNA, which is one of the most prominent source of conflict.
The Future of Stem Cell Research:
Did you know that theyactually last to to 14 days in your body? Yet the results are there for a lot longer, because they are stimulating and creating extracellular vessicles, exosomes, which are the ones actually doing all the regenerative work in the cells and tissues.
As research into stem cells continues to advance, the potential for transformative therapies and medical breakthroughs is immense. From regenerating damaged tissues to treating a wide range of diseases, stem cells hold the promise of improving the lives of millions of people around the world.
However, realizing this potential will require continued investment in research, rigorous testing of therapies, and careful consideration of ethical implications. With continued dedication and innovation, stem cell research has the power to revolutionize medicine and usher in a new era of healthcare.
Yours in Health,
Beth Shaw
Make America Healthy Podcast
© 2024 Make America Healthy. All Rights Reserved
